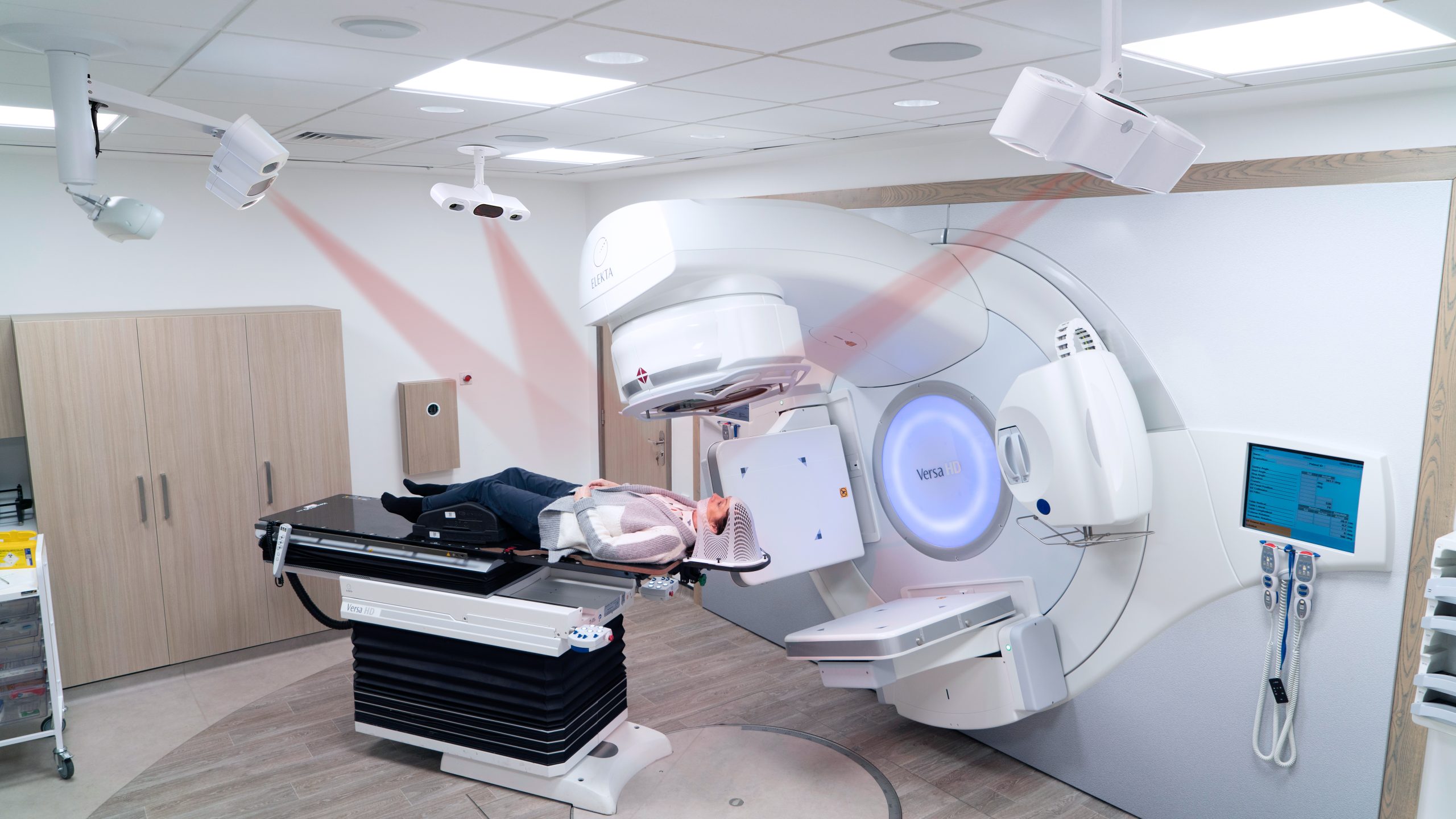
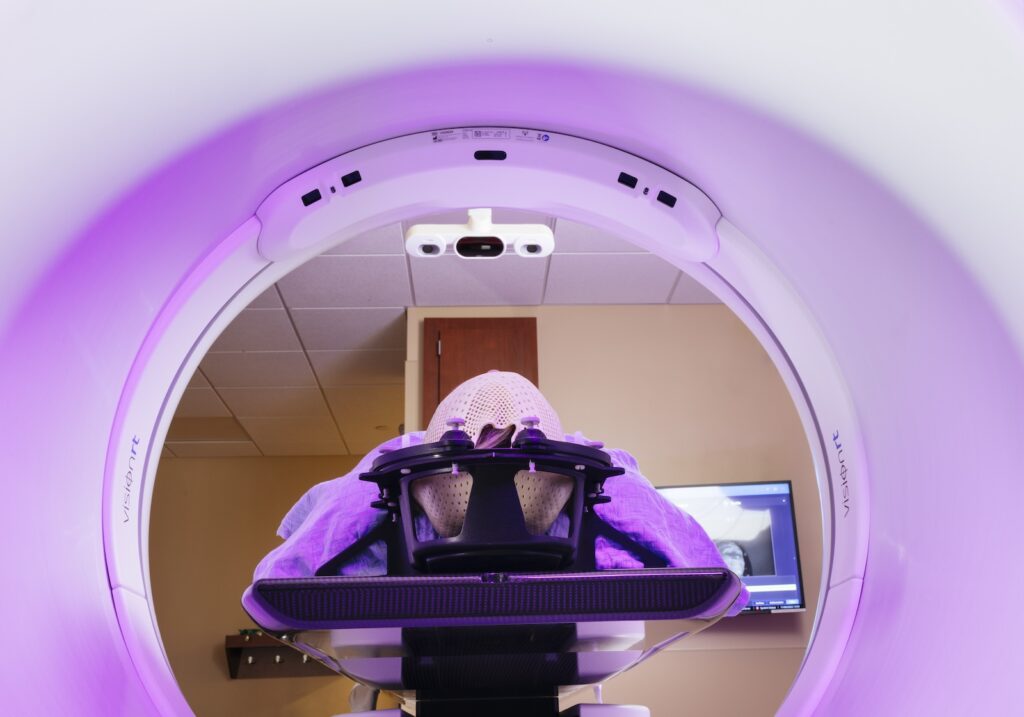
AlignRT for SRS:
Sub-Millimetric Accuracy, Real-Time Tracking, and Seamless Workflows
While full-face masks have traditionally been used for Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS), growing evidence shows that open-face masks, together with SGRT, offer an evidence-based alternative, improving patient comfort1 while ensuring the precision required for effective SRS.
AlignRT supports a frameless, open-face mask approach to deliver sub-millimeter accuracy while helping to enhance patient comfort. Its tracking precision remains within ~0.5mm / 0.2 degrees across all couch rotations and for all skin tones2-5, aligning with stereotactic SGRT recommendations6,7.
MapRT further enhances SRS treatments by disclosing options for different couch angles and longer, safer arcs. These have already been shown to deliver Conformity Index and dose gradient improvements over standard SRS planning techniques8.
DoseRT adds another layer of precision with real-time dose visualization, improving treatment quality and confidence. Together, these technologies support accurate, comfortable, and streamlined SRS delivery.
Find out more about our SRS Module.
Benefits of SRS Treatments with SGRT:
Proven Clinical Outcomes
A study on the use of OSMS for patient positioning found that it was effective throughout all treatment sessions. Patients treated with Single-Isocenter Multitarget (SIMT) radiosurgery in 1 to 5 fractions experienced strong local tumor control with manageable toxicity. The median overall survival was 13.2 months, with a median time of 6.3 months before intracranial disease progression9.
Patient Comfort & Experience
A retrospective study on open-face mask immobilization found that a surface-guided procedure is a step forward in improving patient comfort and positioning accuracy in the same process. Minimized initial setup errors and repositioning rate had been achieved10.
Frameless SRS & Reduced Treatment Time
A study on surface imaging-guided radiosurgery (SIG-RS) found that it offers clinical outcomes comparable to traditional frame-based and frameless SRS techniques for treating brain metastases. Additionally, the use of an open-face mask improved patient comfort while enabling faster treatment times11.
SRS workflow with SGRT:
Plan
MapRT provides the freedom to explore a greater variety of non-coplanar beams, optimizing target conformality while decreasing the dose to organs at risk (OAR). This clearance mapping tool eliminates the need for complicated re-plans and QA checks, streamlining the workflow. By removing the necessity for dry runs, it further reduces the number of patient visits, improving overall treatment efficiency.
Treat
Dose
DoseRT provides additional reassurance by offering real-time in-vivo images of dose delivery while simultaneously monitoring patient positioning, ensuring optimal treatment quality.
Hear from users on their clinical experiences:
- Zhou et al. (2022). Initial clinical experience of surface guided stereotactic radiation therapy with open-face mask immobilization for improving setup accuracy: a retrospective study. Radiation Oncology (London, England), [online] 17(1), p.104. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-022-02077-4.
- Covington et al. (2019). Optical surface guidance for submillimeter monitoring of patient position during frameless stereotactic radiotherapy. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 20(6), pp.91–98. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12611.
- Wiant et al. (2018). Direct comparison between surface imaging and orthogonal radiographic imaging for SRS localization in phantom. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, [online] 20(1), pp.137–144. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12498.
- Sarkar et al. (2018). An evaluation of the consistency of shifts reported by three different systems for non-coplanar treatments. Journal of radiosurgery and SBRT, [online] 5(4), pp.323–330. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30538893/.
- Covington et al. (2020). “Surface guided imaging during stereotactic radiosurgery with automated delivery.” Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics. 2020 Dec;21(12):90-95
- Al‐Hallaq et al. (2022). AAPM task group report 302: Surface‐guided radiotherapy. Medical Physics, 49(4). doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.15532 .
- Freislederer et al. (2022). ESTRO-ACROP guideline on surface guided radiation therapy. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 173, pp.188–196. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2022.05.026.
- Tallhamer, M. (2025). “Implementation Strategies for MapRT”. Presentation at SGRT Poland.
- Palmer et al. (2020). Single-Isocenter Multitarget Stereotactic Radiosurgery Is Safe and Effective in the Treatment of Multiple Brain Metastases. Advances in Radiation Oncology, 5(1), pp.70–76. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2019.08.013.
- Zhou et al. (2022). Initial clinical experience of surface guided stereotactic radiation therapy with open-face mask immobilization for improving setup accuracy: a retrospective study. Radiation Oncology (London, England), [online] 17(1), p.104. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-022-02077-4.
- Pan et al. (2012). Frameless, Real-Time, Surface Imaging-Guided Radiosurgery. Neurosurgery, 71(4), pp.844–852. doi:https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0b013e3182647ad5.
- Pan et al. (2012). Frameless, Real-Time, Surface Imaging-Guided Radiosurgery. Neurosurgery, 71(4), pp.844–852. doi:https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0b013e3182647ad5.
- Pham et al. (2014). Frameless, real-time, surface imaging-guided radiosurgery: update on clinical outcomes for brain metastases. Translational Cancer Research, [online] 3(4). doi:https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2218-676X.2014.07.08.
- Lau et al. (2017). Clinical efficacy and safety of surface imaging guided radiosurgery (SIG-RS) in the treatment of benign skull base tumors. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 132(2), pp.307–312. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2370-7.
Get in touch
Ready to take the next step?
Vision RT’s family of SGRT solutions guide radiation therapy for better patient care at every step: Sim, Planning, Treatment and Dose. Whether you’re looking for a quote, a product demo (virtual or in-person) or just more information, please get in touch.