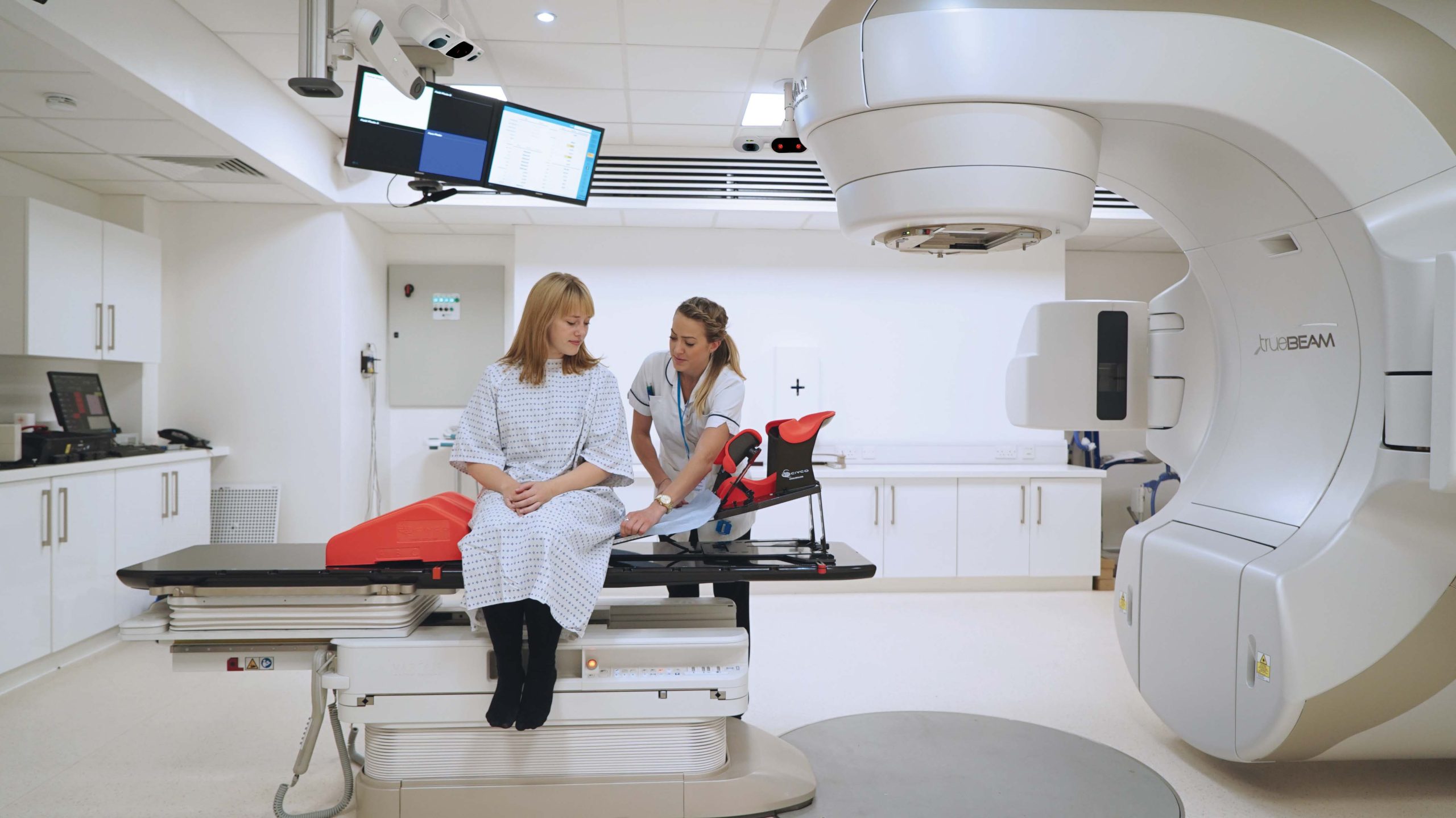
“Traditionally SBRT technologies have offered gains in accuracy but often at the cost of things like efficiency, customization, and comfort for the patient; current evidence seems to suggest that SGRT has overcome this trade-off challenge.”
Enhance SBRT Precision and Patient Comfort with Sub-Millimeter Accuracy and Non-Invasive Motion Tracking
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT/SABR) demands exceptional positional accuracy to precisely target tumors while protecting healthy tissue. However, traditional methods often require rigid immobilization and repeated imaging, increasing complexity, discomfort, and treatment time. Additionally, tumor motion can lead to larger-than-necessary target volumes, risking unnecessary radiation exposure to surrounding tissues.
AlignRT offers 0.5mm accuracy for both standard and breath-hold SBRT, tracking patient movement in real-time with non-invasive, contact-free technology.This advanced system is designed to:
- Help reduce the need for rigid immobilization¹ to improve patient comfort
- Assist in hypofractionated treatments by tracking patient motion in real-time across six degrees of freedom
- Support breath-hold techniques to help manage tumor motion and optimize treatment volume
- Reduce the need for repeat imaging, simplifying workflows
- Automatically pause radiation delivery if the patient moves out of position
- Provide a Respiratory Module that supports phase and amplitude-based gating techniques with six degrees of motion management, providing flexible tools to meet the specific individual needs of the patient.
Benefits of SBRT Treatments with SGRT:
Enhanced Accuracy
AlignRT tracks patients in real-time during the entire treatment delivery procedure with sub-mm and sub-degree accuracy2,3,4. It is the ideal choice for both breath-hold and free-breathing SBRT treatment delivery.
Workflow Optimization
Patient Comfort
AlignRT is completely non-contact and non-ionizing; there is no need to immobilize patients or use external or internal markers. AlignRT is clinically proven to be as accurate as solutions relying on additional internal imaging9,10.
Time Efficient
AlignRT provides a consistent and efficient workflow for SBRT delivery and no extra equipment is required. Treatments can be completed in the same amount of time, with minimal impact on capacity and throughput11,12.
SBRT/SABR Workflow with SGRT:
Sim
SimRT and Real-Time Coach provide contactless breath-hold training, minimizing infection risk and improving patient compliance. A recent study13 found SimRT to be 3x more accurate than physical surrogates in predicting tumor movement with 4DCT.
Plan
MapRT provides the freedom to explore a greater variety of non-coplanar beams, optimizing target conformality and reducing the dose to organs at risk (OAR). This tool can help optimize the beam configuration14, streamlining the treatment process.
Treat
AlignRT is designed to ensure high positional accuracy at all couch angles, fully compliant with ESTRO and AAPM guidelines. With a patient-centric approach, it minimizes immobilization15 and enables the use of open-face masks to enhance comfort. Additionally, the Respiratory Module offers new possibilities for phase, amplitude and backup gating.
Dose
DoseRT enhances precision by verifying that the patient remains in the correct position throughout the treatment session. Capturing real-time imaging of dose delivery, allows clinicians to detect and correct any unintended shifts, ensuring the prescribed dose is accurately delivered to the target while minimizing exposure to surrounding organs.
Hear from users on their clinical experiences:
- Wei et al. (2020). Quantifying the impact of optical surface guidance in the treatment of cancers of the head and neck. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 21(6), pp.73–82. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12867.
- Wen et al. (2016). Technical Note: Evaluation of the systematic accuracy of a frameless, multiple image modality guided, linear accelerator based stereotactic radiosurgery system. Medical Physics, 43(5), pp.2527–2537. doi:https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4947199.
- Covington E, et al. (2018) Submillimeter monitoring of intrafraction patient movement with optical surface imaging. AAPM Annual Meeting.
- Waghorn, B. (2018). Advanced Camera Optimization White Paper 1. [online] Available at: https://visionrt.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Advanced-Camera-Optimization-White-Paper.pdf.
- Heinzerling et al., (2017). Use of 3D Optical Surface Mapping for Quantification of Interfraction Set up Error and Intrafraction Motion during Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Treatments of the Lung and Abdomen. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics, [online] 99(2), p.E670. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.06.2215.
- Leong, B. and Padilla, L. (2019). Impact of use of optical surface imaging on initial patient setup for stereotactic body radiotherapy treatments. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 20(12), pp.149–158. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12779.
- Herron, E, et al. (2018). Surface Guided Radiation Therapy as a Replacement for Patient Marks in Treatment of Breast Cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics, 102(3), pp.e492–e493. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.07.1400.
- Allen, B. and Ramtohul, M. (2020). Markerless radiotherapy at the Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham. Radiography, 26, pp.S8–S9. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radi.2019.11.023.
- Sarkar, et al. (2018). An evaluation of the consistency of shifts reported by three different systems for non-coplanar treatments. Journal of radiosurgery and SBRT, [online] 5(4), pp.323–330. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30538893/.
- Wiant, at al. (2018). Direct comparison between surface imaging and orthogonal radiographic imaging for SRS localization in phantom. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, [online] 20(1), pp.137–144. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12498.
- Menyhart G. (2016) “SGRT for Breath Hold SBRT: A Measured Respons.” SGRT Annual Meeting, Atlanta
- Lawson J. (2019) “Surface Guided Radiation Therapy (SGRT) in SRS and SBRT. Advances in Accuracy and Elevating Patient Experience” SGRT Annual Meeting, Sydney
- Qubala et al., (2023). Comparative evaluation of a surface-based respiratory monitoring system against a pressure sensor for 4DCT image reconstruction in phantoms. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, [online] p.e14174. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.14174.
- Gonod et al. (2025). Benchmarking MapRT and first clinical experience: A novel solution for collision‐free non‐coplanar treatment planning. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.14572.
- Wei, W., Ioannides, P.J., Sehgal, V. and Daroui, P. (2020). Quantifying the impact of optical surface guidance in the treatment of cancers of the head and neck. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 21(6), pp.73–82. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12867.
Get in touch
Ready to take the next step?
Vision RT’s family of SGRT solutions guide radiation therapy for better patient care at every step: Sim, Planning, Treatment and Dose. Whether you’re looking for a quote, a product demo (virtual or in-person) or just more information, please get in touch.