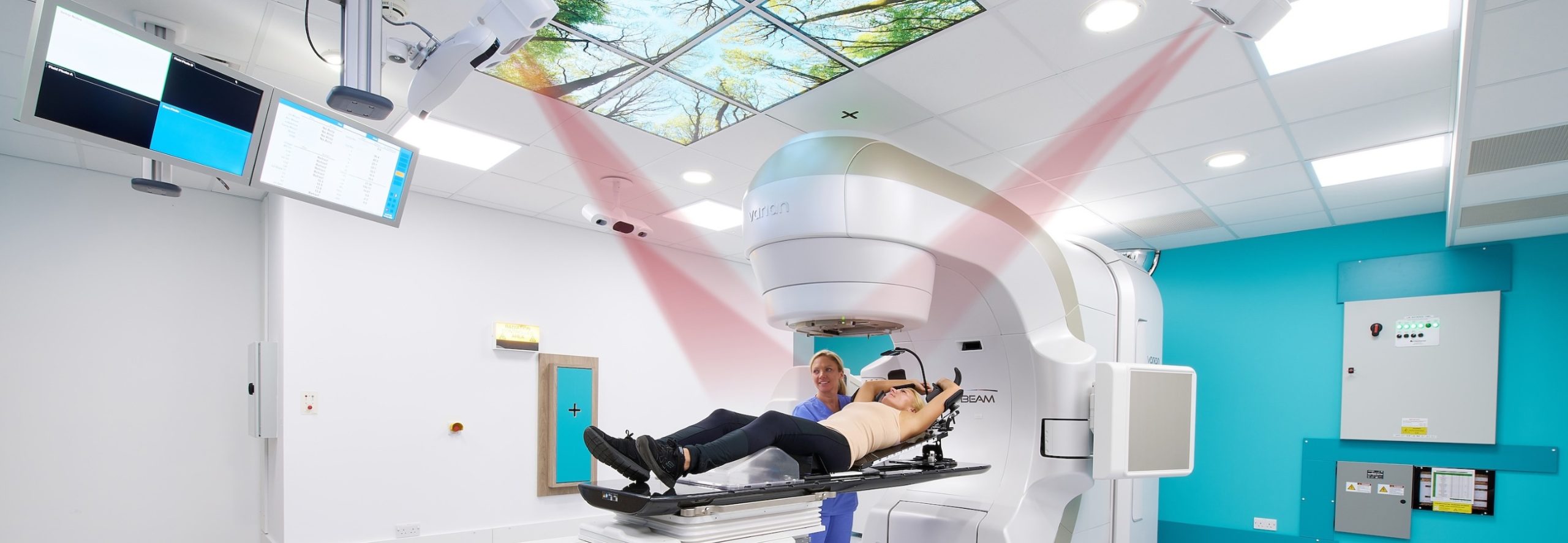
Our SGRT DIBH Solutions: Safer for Patients, More Efficient for Clinics
The proximity of the left breast to the heart can leave the heart vulnerable to radiation exposure during left breast radiotherapy. This can lead to serious long-term cardiac complications¹.
To minimize this risk, many centers use Deep Inspiration Breath Hold (DIBH), to move the heart away from the breast during treatments. Implementing DIBH can be challenging². Patients breathe in different ways, in different rhythms, and may inadvertently arch their back in a way that simulates a deep breath. Without an accurate way to track and monitor breaths in all six degrees of freedom, a good separation of heart and left breast can be difficult to achieve.
AlignRT is the only SGRT system with long-term data showing avoidance of cardiac damage in left-breast cancer.
There are many papers on the clinical benefits of Vision RT’s SGRT solutions for DIBH. AlignRT uses non-invasive, contact-free technology to track the skin’s surface and ensure alignment with the treatment plan’s ideal position with sub-millimetric precision, providing increased confidence in sparing critical organs. It also has been shown to help reduce treatment times by an average of 22% per fraction3-9.
Research on DIBH Treatments with SGRT:
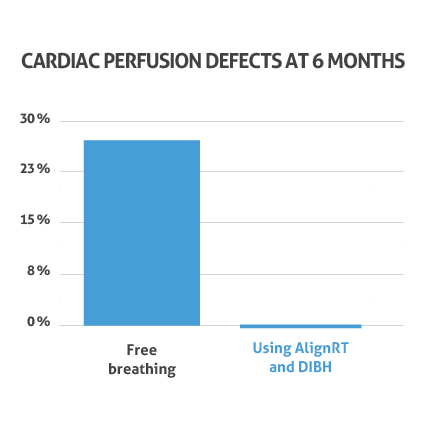
| During a study at the University of North Carolina, patients were treated using AlignRT for DIBH. Of these, 0% exhibited radiation-induced abnormalities in blood flow to the heart six months after treatment¹⁰.
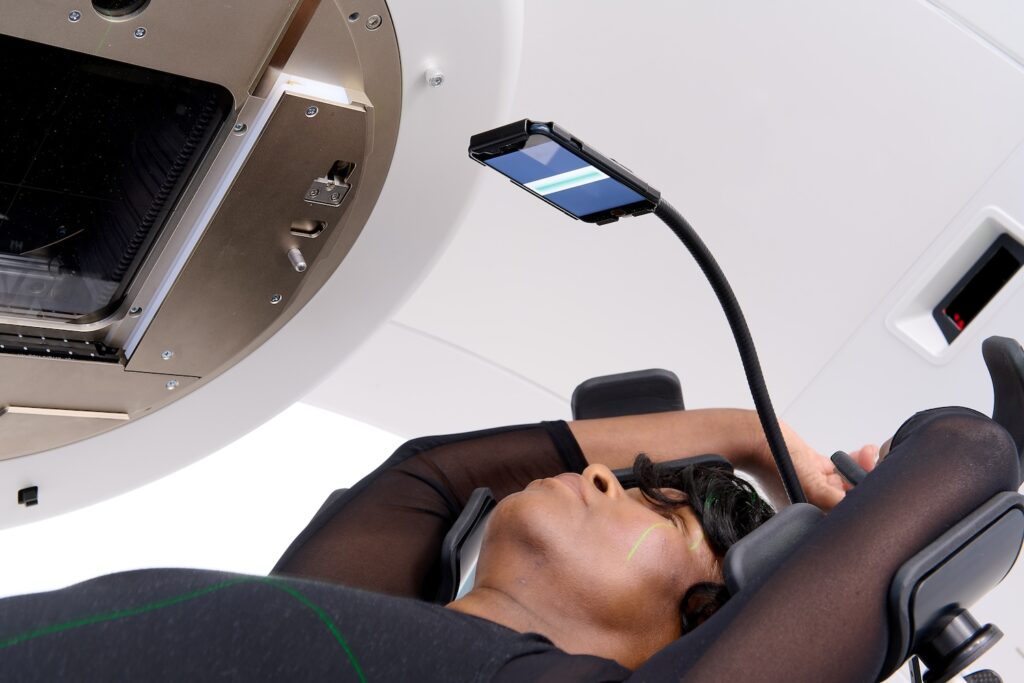
There are many published papers covering the use of AlignRT for DIBH, and accessories are available to make DIBH with AlignRT even simpler for the patient and therapist. Learn more about our RealTime Coach Display, to simplify patients’ breath-hold. |
 |
A study titled “Setup Margins Based on Inter- and Intrafractional Setup Errors in Left-Sided Breast Cancer Radiotherapy Using Deep Inspiration Breath-Hold (DIBH) and Surface Guided Radiotherapy (SGRT)⁴” revealed:
- Improved Intrafractional Accuracy: Intrafractional patient setup accuracy outperformed interfractional accuracy (p < 0.001).
- Minimized Setup Margins: Setup margins based solely on SGRT were 4 mm (lateral), 6 mm (longitudinal), and 4 mm (vertical), with intrafractional error contributing ≤1 mm. Setup margins based solely on SGRT were, on average, 5mm in all directions
- Efficiency and Safety: SGRT reduces the need for repeat kV-CBCT imaging, saving time and minimizing radiation exposure.
AlignRT has been shown to help reduce DIBH treatment times by an average of 22% per fraction3-9.
Deep Inspiration Breath Hold (DIBH) workflow with SGRT:
Sim
SimRT and Real-Time Coach provide contactless breath-hold training, minimizing infection risk and improving patient compliance. A recent study¹² found SimRT to be 3x more accurate than physical surrogates in predicting tumor movement with 4DCT.
Plan
MapRT simplifies non-coplanar treatments, which have been shown to reduce heart dose¹³. It can ensure patient safety by verifying that elbows remain clear of the gantry at all angles and checking for potential collisions when the couch is rotated. This allows for improved treatment planning, even when Deep Inspiration Breath Hold (DIBH) is not feasible14-15.
Treat
AlignRT enhances Deep Inspiration Breath Hold (DIBH) treatments, ensuring accurate patient positioning throughout treatment, reducing the risk of cardiac perfusion defects to 0% after six months10, while helping to reduce treatment times by an average of 22% per fraction3-9.
Dose
DoseRT integrates Cherenkov imaging with AlignRT cameras to provide real-time feedback on dose distribution and patient positioning, enhancing safety and reducing errors. Studies show Cherenkov imaging can detect treatment errors in 10% of patients16, while 2.6% of breast cancer patients develop secondary contralateral cancer due to radiation exposure17.
Hear from users on their clinical experiences:
1. Darby et al., (2013). Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease in Women after Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 368(11), pp.987–998. doi:https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1209825.
2. Gierga et al., (2012). A Voluntary Breath-Hold Treatment Technique for the Left Breast With Unfavorable Cardiac Anatomy Using Surface Imaging. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics, 84(5), pp.e663–e668. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.07.2379.
3. Giantsoudi, PhD, et al., (2022). Tattoo Free Set-up for Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Regional Nodal Irradiation. Practical Radiation Oncology. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2022.08.001.
4. Mueller, et al., (2023). Accuracy and Efficiency of Patient Setup Using Surface Imaging versus Skin Tattoos for Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation. Advances in Radiation Oncology. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2023.101183.
5. Sauer, TO, et al., (2023). Prerequisites for the clinical implementation of a markerless SGRT-only workflow for the treatment of breast cancer patients. Strahlentherapie und Onkologie, 199, pp. 22–29. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01966-7.
6. Wei, et al., (2020). Quantifying the impact of optical surface guidance in the treatment of cancers of the head and neck. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 21, pp. 73–82. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12867.
7. Hickey, et al., (2021). Surface Guided Radiotherapy (SGRT) vs Varian RPM for deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) breast treatments. Physica Medica, 81, pp. 14-21. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.01.021.
8. Kang, S., Jin, H., Chang, J.H., et al., (2023). Evaluation of initial patient setup methods for breast cancer between surface-guided radiation therapy and laser alignment based on skin marking in the Halcyon system. Radiation Oncology, 18, 60. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-023-02250-3.
9. Flores-Martinez, et al., (2020). Assessment of the use of different imaging and delivery techniques for cranial treatments on the Halcyon Linac. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 21, pp. 53–61. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12772.
10. Zagar et al., (2015). Prospective assessment of deep inspiration breath hold to prevent radiation-associated cardiac perfusion defects in patients with left-sided breast cancer. Journal of clinical oncology, 33(28_suppl), pp.41–41. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2015.33.28_suppl.41.
11. Rudat et al., (2024). Setup margins based on the inter‐ and intrafractional setup error of left‐sided breast cancer radiotherapy using deep inspiration breath‐hold technique (DIBH) and surface guided radiotherapy (SGRT). Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.14271.
12. Qubala et al., (2023). Comparative evaluation of a surface-based respiratory monitoring system against a pressure sensor for 4DCT image reconstruction in phantoms. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, [online] p.e14174. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.14174.
13. J et al., (2023). Locoregional breast radiotherapy including IMN: optimizing the dose distribution using an automated non-coplanar VMAT-technique. Acta oncologica (Stockholm, Sweden), [online] 62(10). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2023.2264488.
14. Xie et al., (2020). Postmastectomy radiotherapy for left-sided breast cancer patients: Comparison of advanced techniques. Medical Dosimetry, [online] 45(1), pp.34–40. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2019.04.005.
15. Xu et al., (2021). Non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy for locoregional radiotherapy of left-sided breast cancer including internal mammary nodes. Radiology and Oncology, 55(4), pp.499–507. doi:https://doi.org/10.2478/raon-2021-0045.
16. Burt et al., (2017). Risk of secondary malignancies after radiation therapy for breast cancer: Comprehensive results. The Breast, 35, pp.122–129. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2017.07.004.
17. Jarvis et al., (2021). Initial Clinical Experience of Cherenkov Imaging in External Beam Radiation Therapy Identifies Opportunities to Improve Treatment Delivery. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics, 109(5), pp.1627–1637. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.11.013.
Get in touch
Ready to take the next step?
Vision RT’s family of SGRT solutions guide radiation therapy for better patient care at every step: Sim, Planning, Treatment and Dose. Whether you’re looking for a quote, a product demo (virtual or in-person) or just more information, please get in touch.