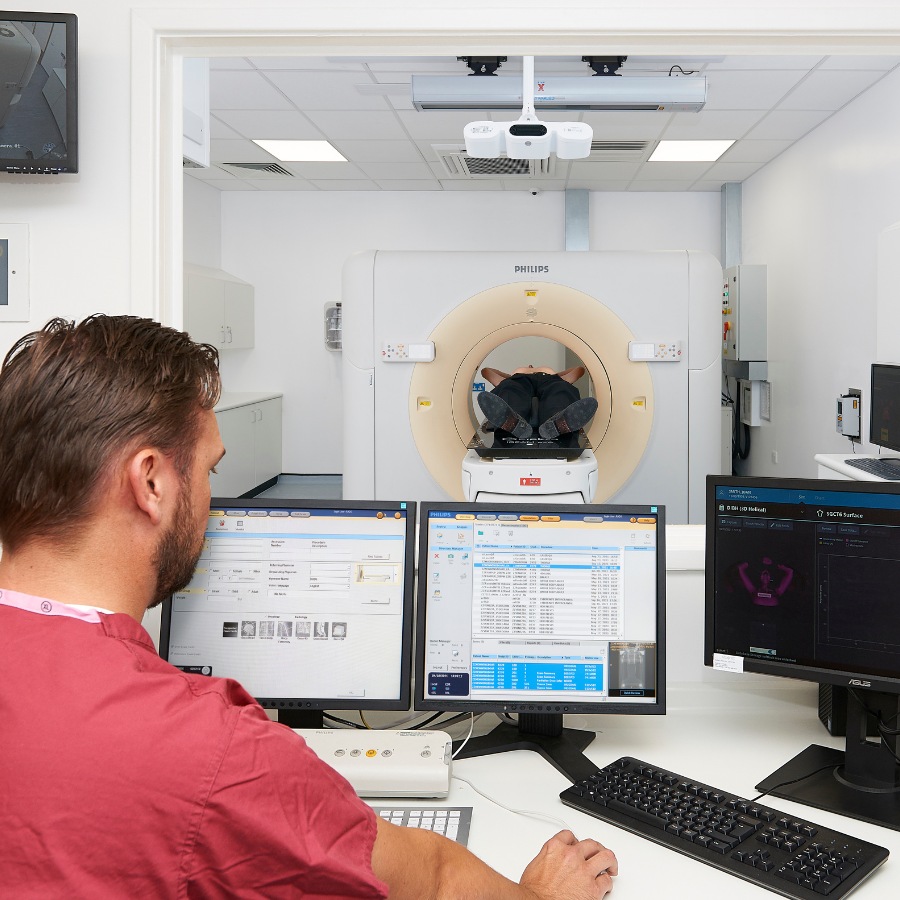
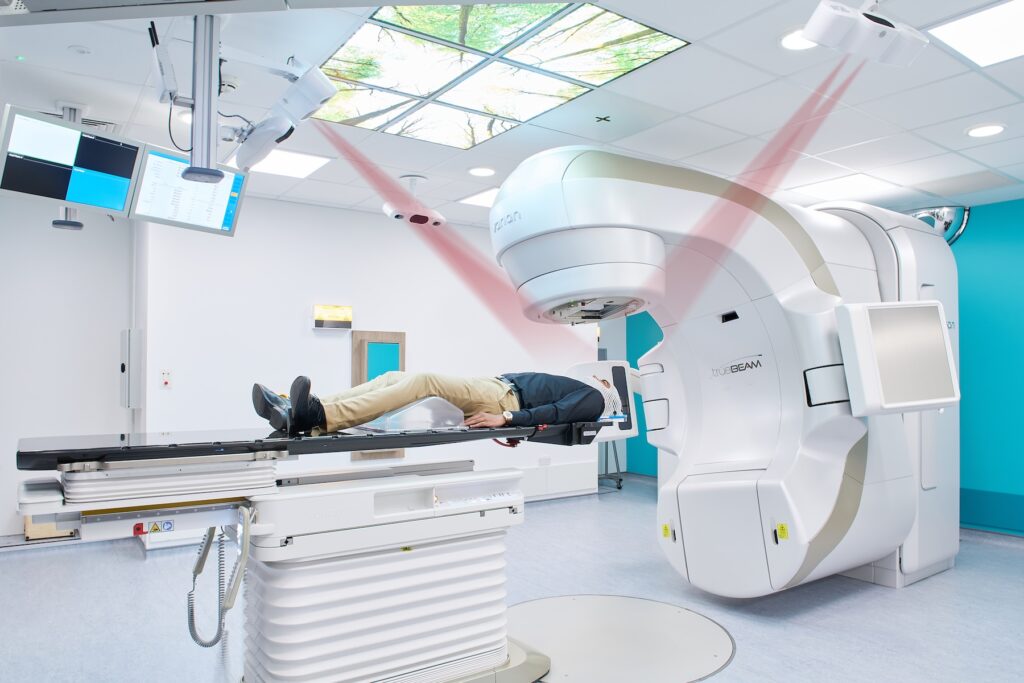
Systèmes en utilisation clinique active dans le monde entier
Nos systèmes sont utilisés dans 24 des 25 meilleurs hôpitaux américains pour le cancer
Résultats cliniques publiés dans des articles de revues à comité de lecture
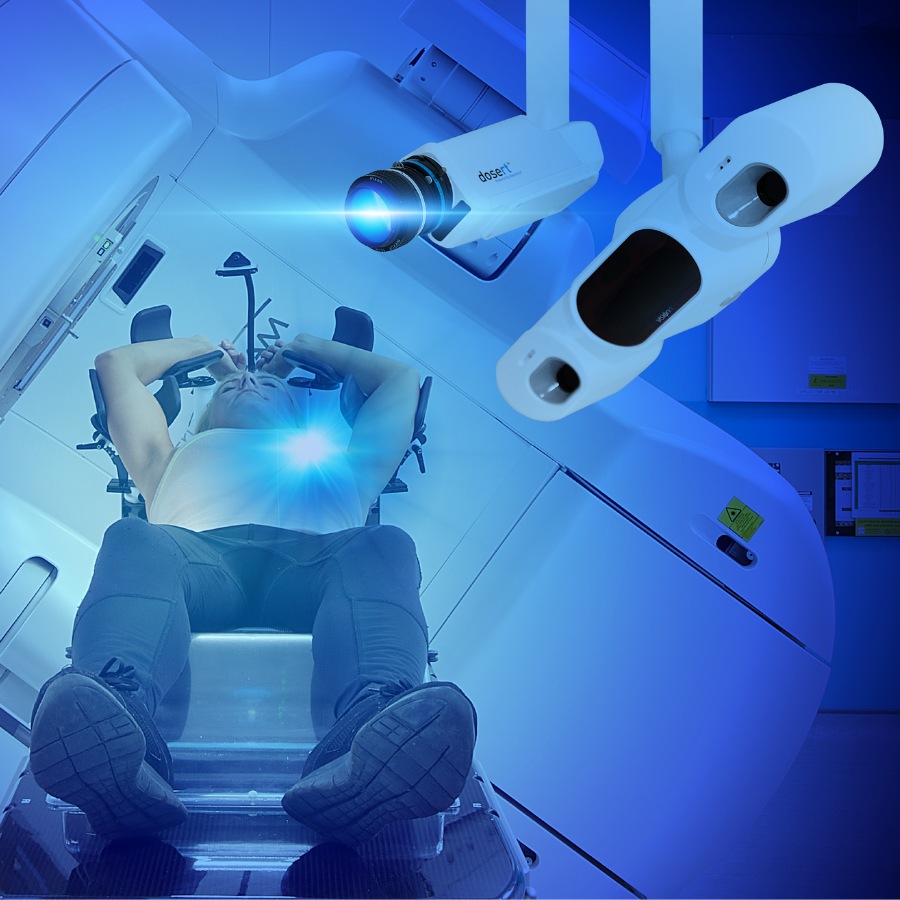
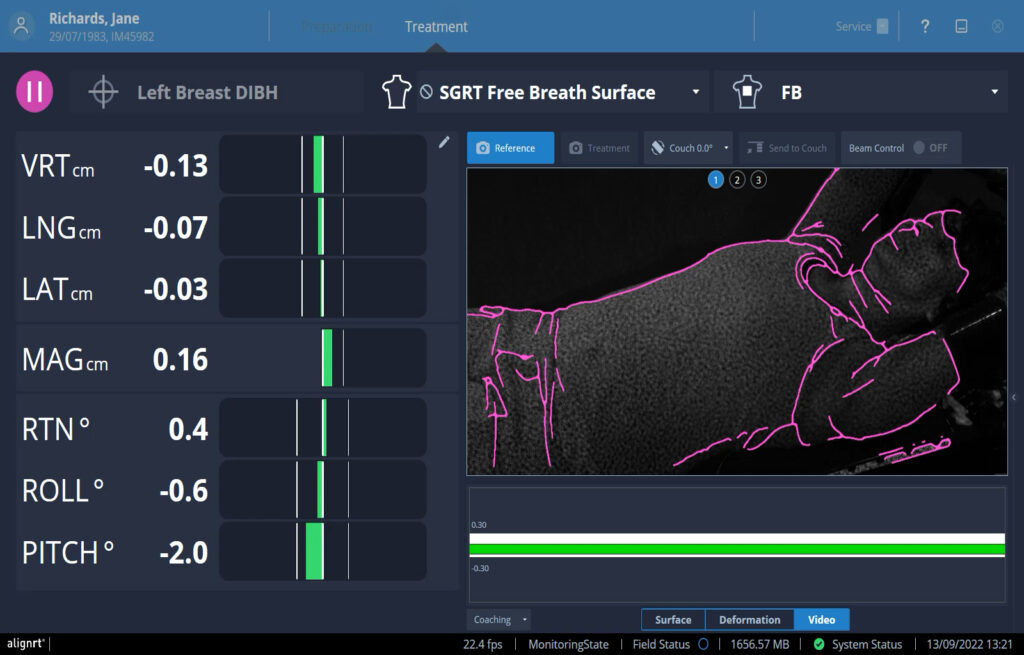
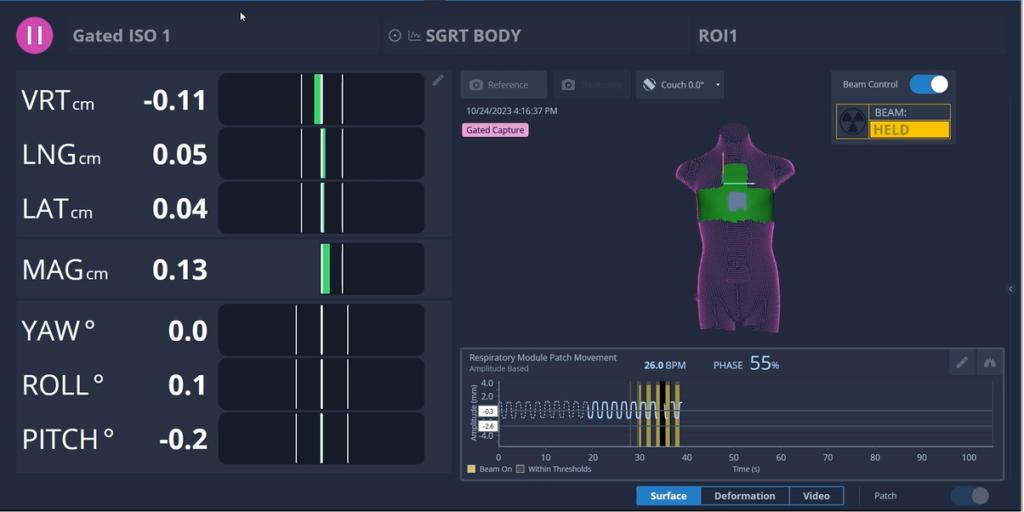
AlignRT peut aider à réduire les temps de traitement de 22% en moyenne par fraction
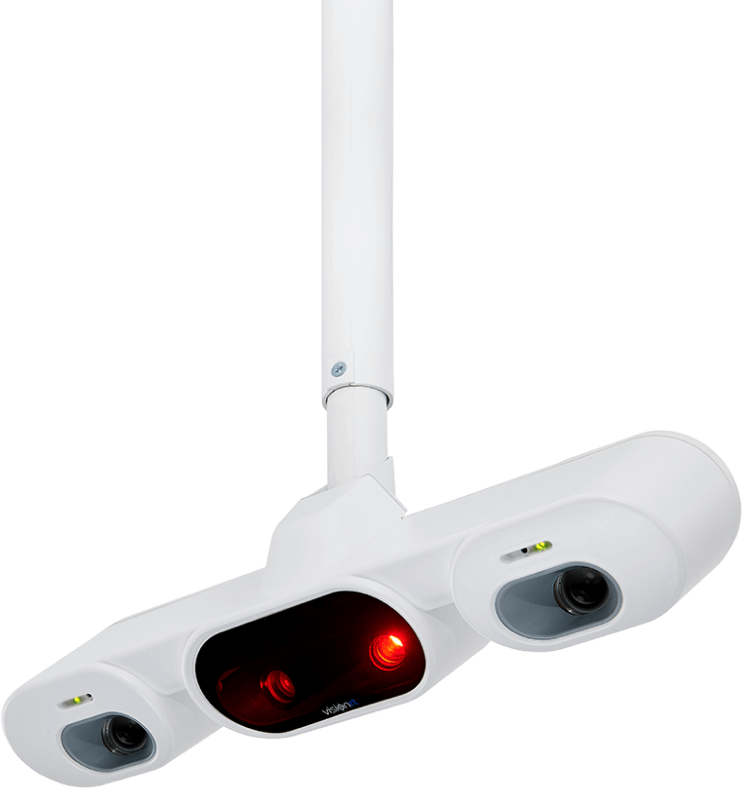
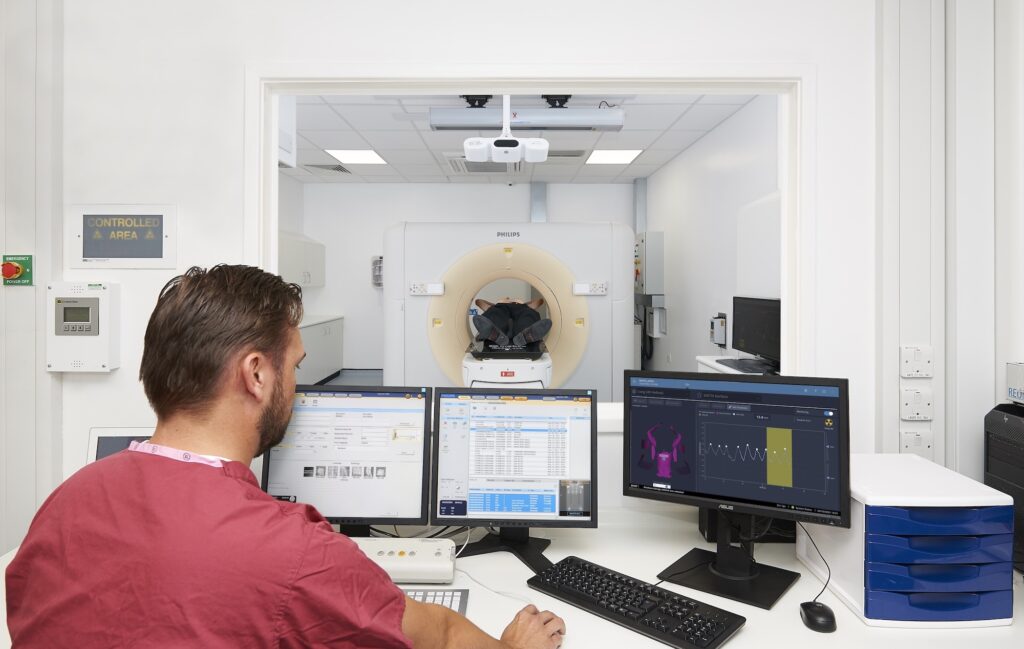
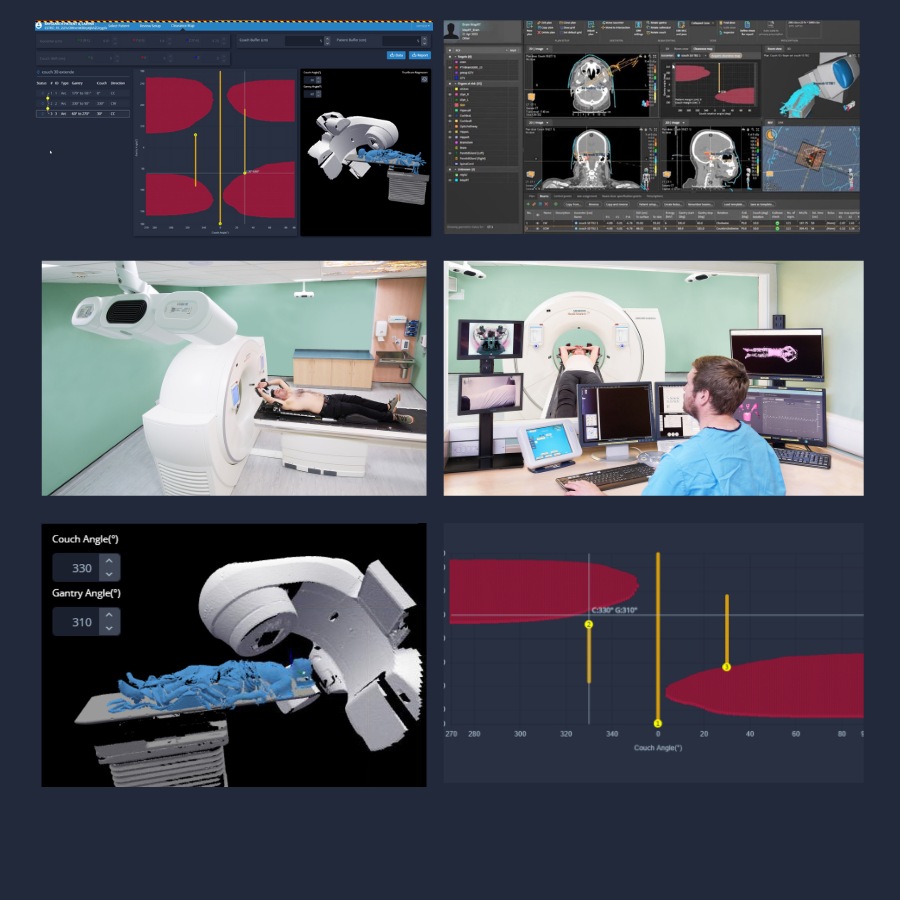
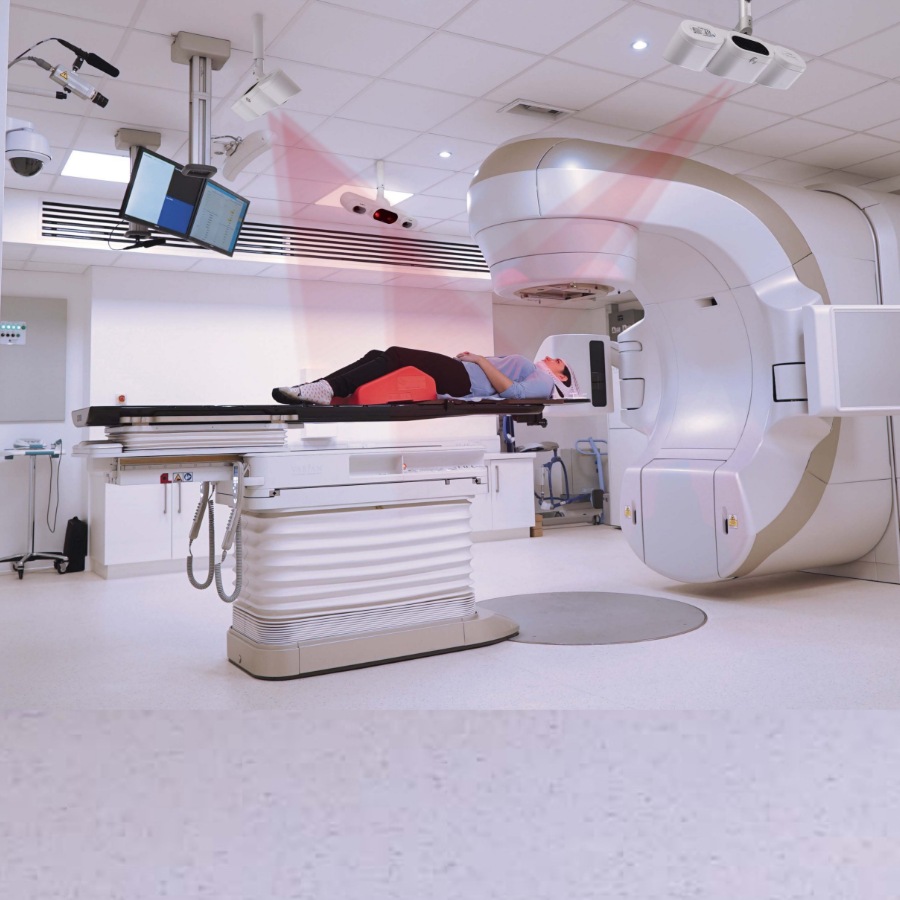
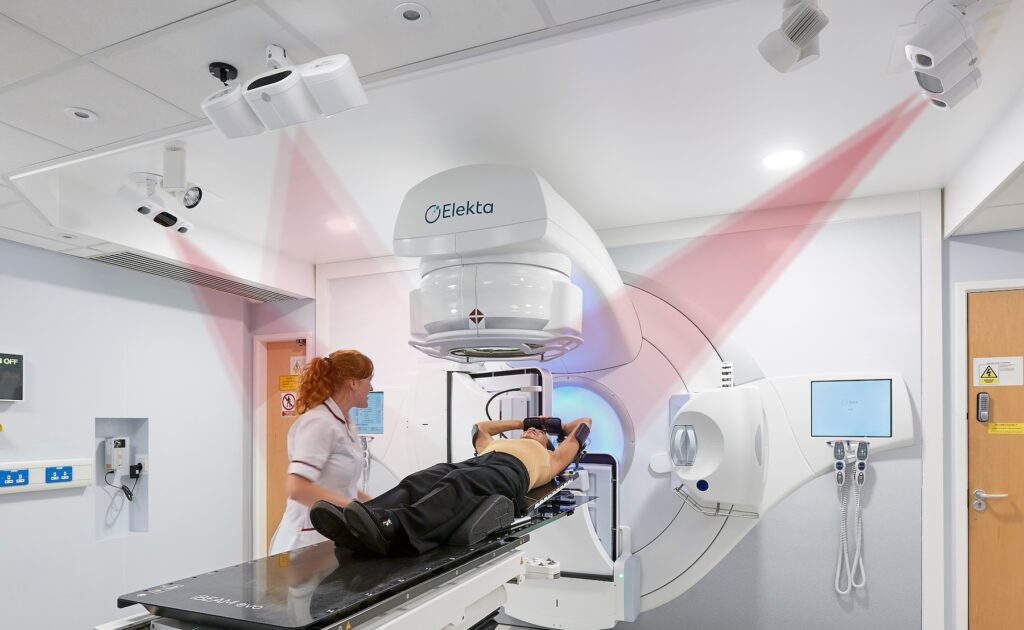
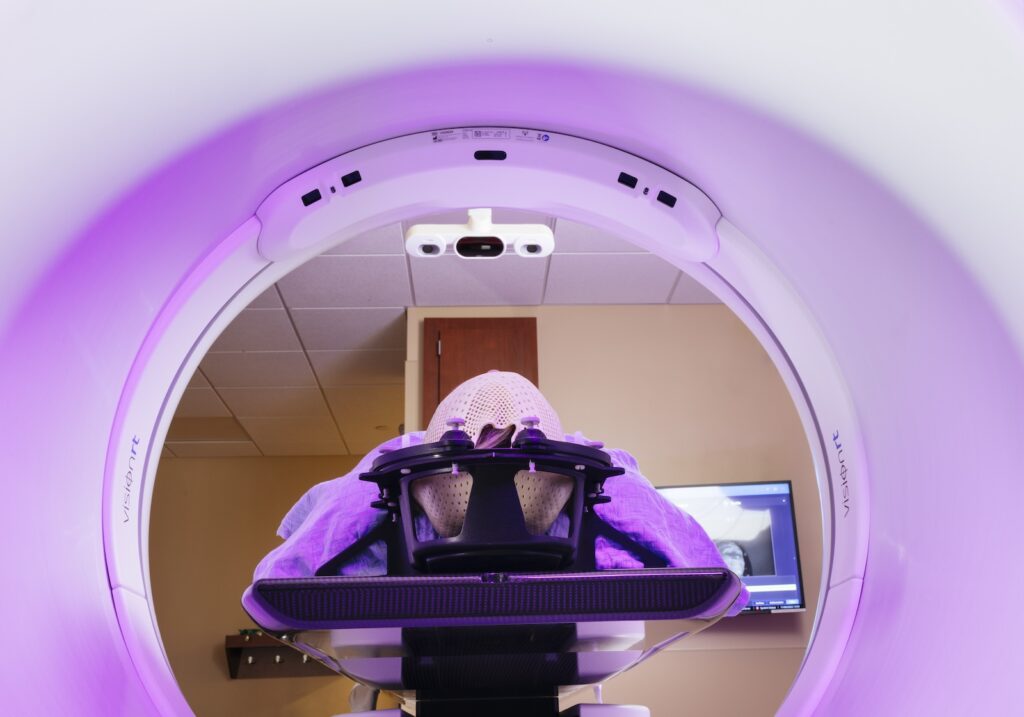
Applications de la SGRT avec AlignRT
Tous les patients, à chaque fraction.
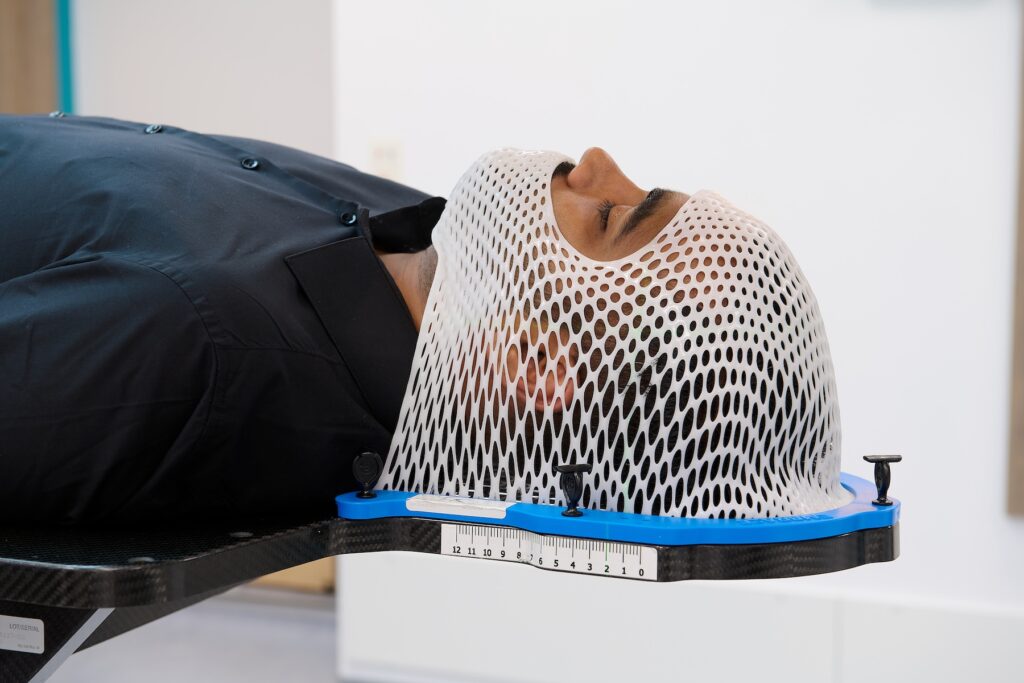
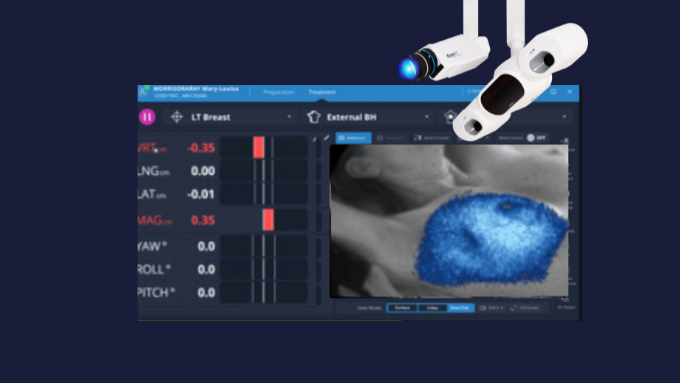
Les solutions SGRT de Vision RT optimisent l’ensemble du traitement de radiothérapie et s’adaptent à tous les types de cancers, dont ceux du sein, du cerveau, du poumon, du foie, les sarcomes, ainsi que les cancers de la prostate, de la tête, du cou, etc.
Notre engagement : une radiothérapie plus efficace pour tous les patients atteints de cancer.
Fort de près de 25 ans d’expérience en SGRT, nos solutions aident les cliniques à dispenser des traitements contre le cancer plus sûrs, plus précis et plus confortables pour les patients.
Dans cette vidéo, des membres de notre équipe partagent ce que cela représente pour eux de faire partie d’une entreprise qui contribue à faire la différence.
Communiqués de presse
Enhancing Head and Neck Treatments: The Impact of AlignRT at Lincoln County Hospital
read article
Vision RT partners with Medical Device HQ for efficiency initiative / training
read article
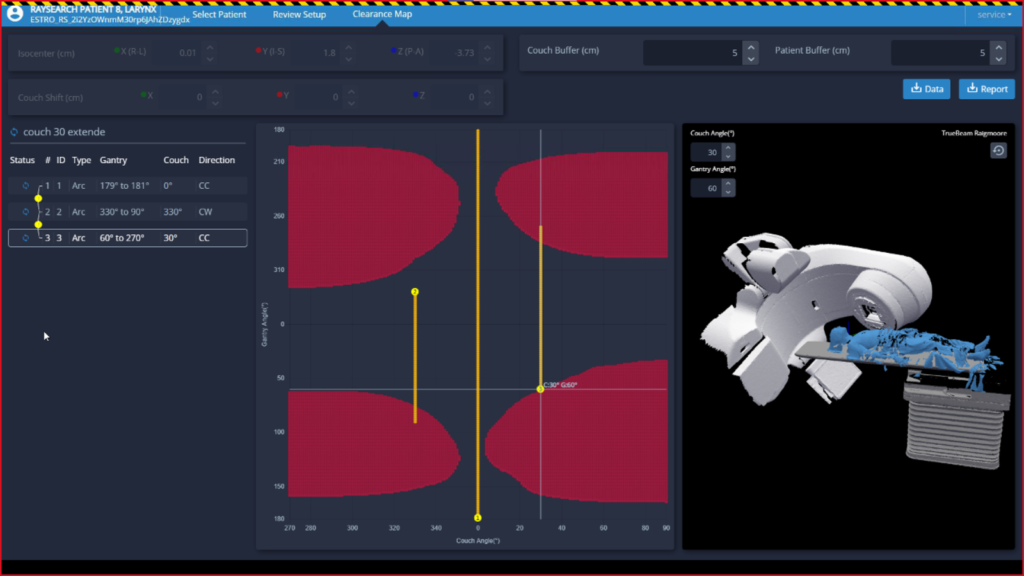
RaySearch Laboratories and Vision RT Unveil Seamless Integration at ESTRO Conference in Vienna
read article