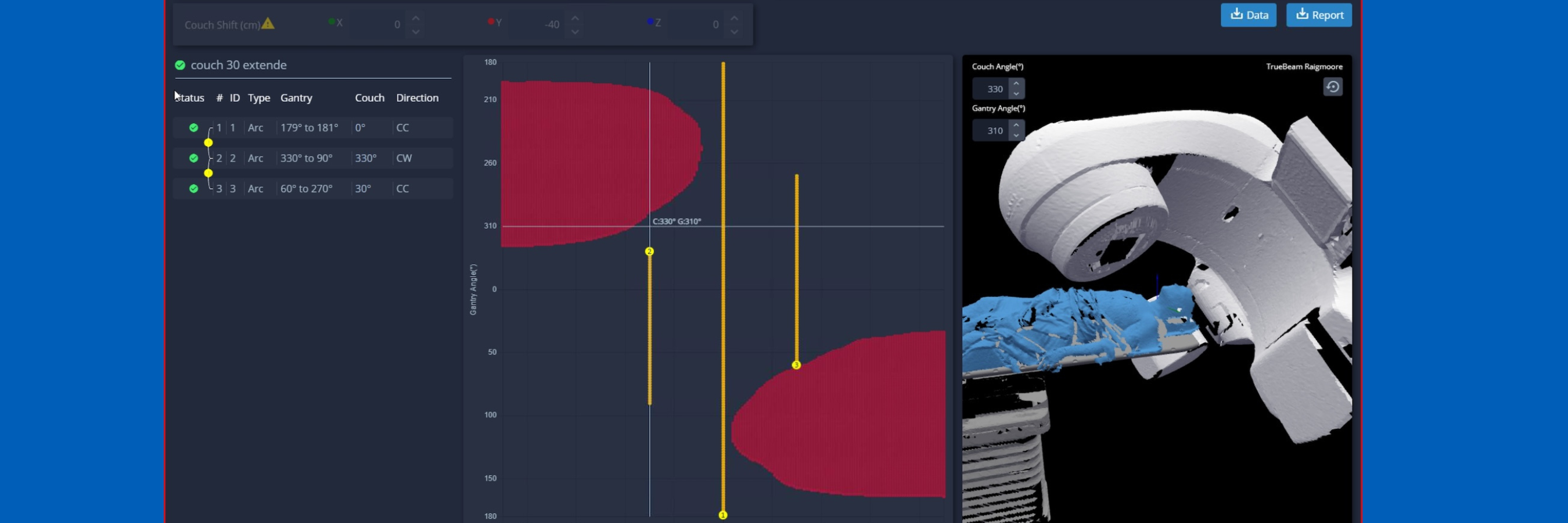
Vereinfachen Sie die Planung nicht-koplanarer Behandlungen
MapRT bildet die gesamte Oberfläche des Patienten und des Zubehörs ab, um Kollisionen in den häufigsten Problembereichen wie den Ellbogen zu erkennen. Darüber hinaus überprüft die Abstandskarte die Sicherheit für alle Liege- und Portalwinkel, sodass Planer Hinweise zur Erhöhung der Liegehöhen und zur Verlängerung der Bögen haben – für bessere Planungen mit zuverlässiger Durchführung der Bestrahlung*.
Klicken Sie hier, um mehr über die Vorteile nicht koplanarer Behandlungen zu erfahren.
Vorteile der Verwendung von MapRT:
Studien zeigen, dass nicht-koplanare Behandlungen klinisch relevante Verbesserungen der Behandlungspläne bewirken können1, insbesondere bei Lungenkrebs 2,3,4,5 Brustkrebs 6,7,8,9 Kopf- und Halskrebs 10,11,12,13,14 und Lymphom 15 ,16 und hochgradiges Gliom 17
Eine aktuelle Studie18 zeigte eine verbesserte Bewertung der durchführbaren Bestrahlung mithilfe von MapRT. Standardplanungsmethoden übersehen 11 % der potenziellen Kollisionen und identifizieren nur 64 % der freien Strahlengänge/Bögen. Mit MapRT wurden 0 % der potenziellen Kollisionen übersehen und 100 % der freien Strahlen/Bögen identifiziert.
Mit der neuen Anwendungsprogrammierschnittstelle (API)* von MapRT können Sie Ihre Nutzung von MapRT zusammen mit Ihrem Behandlungsplanungssystem integrieren und erweitern.
*Derzeit nicht zum Verkauf in den USA verfügbar.“
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Die veröffentlichten Erkenntnisse deuten darauf hin, dass VMAT-Behandlungen zwar eine gute Dosimetrie liefern, nicht-koplanare VMAT-Behandlungen jedoch sogar noch bessere Ergebnisse liefern können, beispielsweise bei Lungenkrebs1,2,3 Brustkrebs4,5,6 und Kopf-/Halskrebs7,8,9.
Die Erfassung der gesamten Patienten- und Zubehöroberfläche während der Simulation dauert normalerweise 1–2 Minuten. Einige der jüngsten MapRT-Arbeiten haben klinisch bedeutsame Planverbesserungen mit einer Verlängerung der Behandlungszeit um 30 Sekunden gezeigt19. MapRT kann dazu beitragen, die Notwendigkeit von Probleläufen zu verringern, und ermöglicht es Kliniken mit der neuen API (derzeit in den USA nicht erhältlich), durch skripting, auf die Clearance-Daten im Behandlungsplanungsystem zuzugreifen.
MapRT ist eine sehr neue Technologie, aber ein Artikel, der deutliche Verbesserungen der Planungsleistung zeigt, ist hier und auf unserer Beweisseite verfügbar. Viele Benutzer auf der ganzen Welt stehen für eine Beratung zum Wert von MapRT zur Verfügung – wenden Sie sich an Vision RT, wenn Sie möchten, dass wir einen Referenzbesuch vor Ort vereinbaren.
Nehmen Sie Kontakt auf
Bei Vision RT legen wir großen Wert auf unsere Reaktionsfähigkeit und unseren Kundenservice.
Ob Sie ein Angebot, eine Demo (virtuell oder persönlich) oder einfach mehr Informationen suchen, nehmen Sie bitte Kontakt mit uns auf bezüglich AlignRT oder einem unserer anderen Produkte: