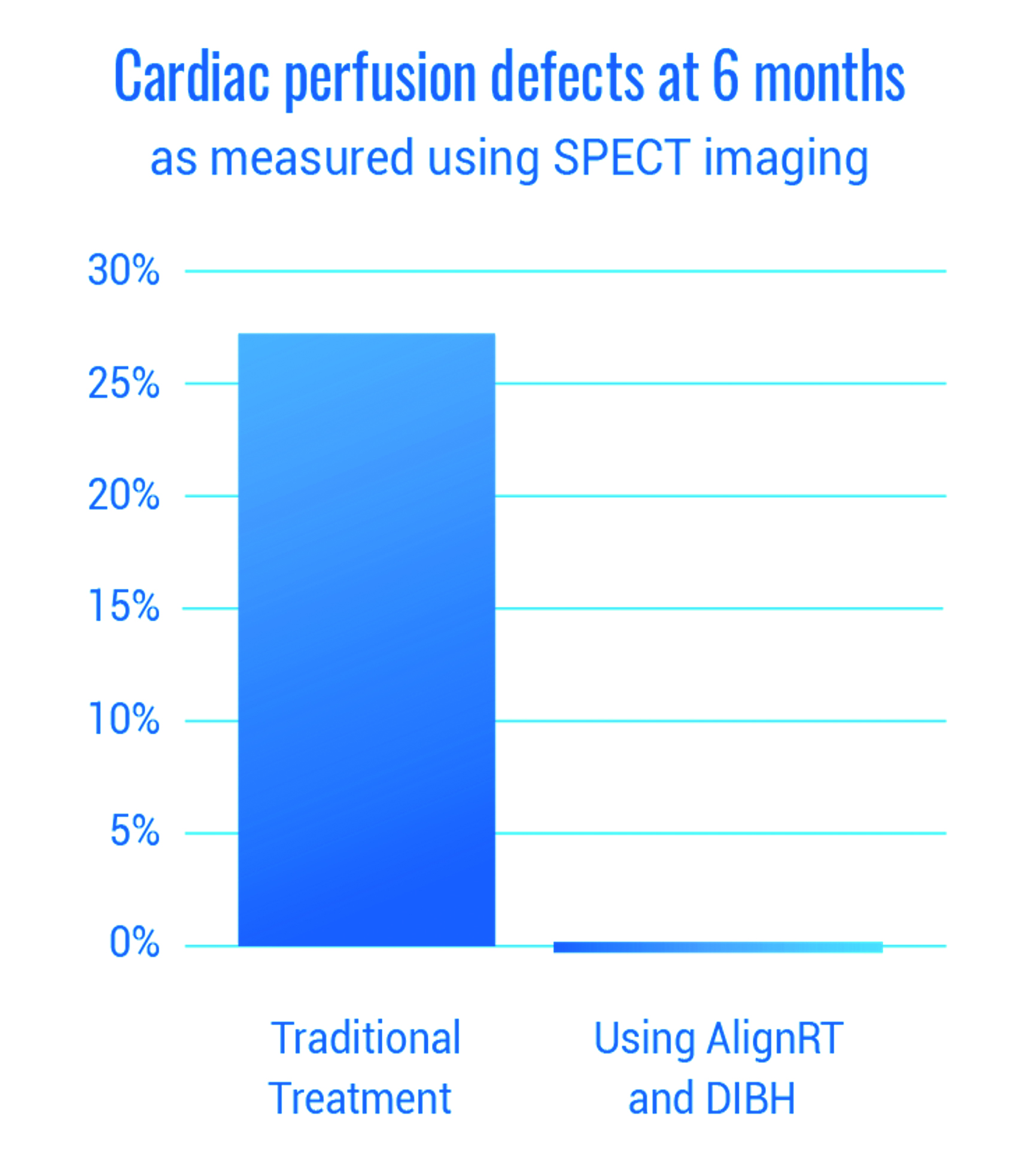
Radiation therapy has been shown to be a highly effective treatment for breast cancer. But the proximity of the left breast to the heart leaves the heart vulnerable to radiation exposure. This has been shown, in some cases, to lead to serious long-term cardiac complications¹.
Many centers are beginning to have patients use Deep Inspiration Breath Hold (DIBH) to move the heart away from the breast during therapy. However, achieving this can be challenging². Patients breathe in different ways at different times and may arch their back to simulate a deep breath in. These different movements can appear similar to a patient’s true breath-hold, but do not necessarily separate the heart from the breast.